How to spray black currants against diseases and pests?
Timely and competent processing of black currants from fungal diseases and pests is the key to preserving the harvest of berries and the health of the bushes. In order to stop the disease in time or stop the spread of a colony of parasites, it is necessary to learn to recognize them by their external signs and to choose the right means.
General processing rules
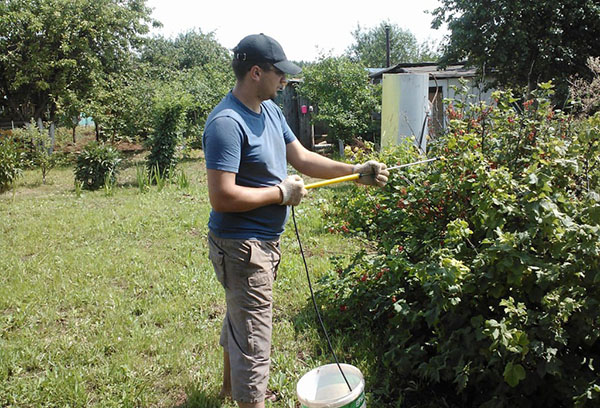
So that spraying the bushes with chemicals does not result in harm to plants and the gardener, a number of rules should be followed:
- work in gloves, closed clothing, headwear, goggles and a mask;
- do not process in windy or rainy weather;
- spray not only the bush, but also the trunk circle;
- be sure to comply with the terms: during the blooming of the buds, antifungal drugs can damage the structure of the flower, burn the delicate leaves. Insecticides will kill the bees, disrupt the pollination process and the ovary.
Important!
In the spring, black currants begin their growing season earlier than other berry bushes.
As for biological products, most of them quickly lose their effectiveness in the sun, so treatments are carried out in the evening.Major pests
Care for black currants is quite simple, but from early spring the bushes are attacked by various pests, traces of which appear during the flowering period and the ovary of berries. To combat them, in addition to a wide range of chemicals, organic insecticides have been developed, for example Fitoverm. The active substance paralyzes the digestive system of the pest, while remaining harmless to pollinators and beneficial insects. It is possible to spray black currants from pests with this drug during the entire growing season.
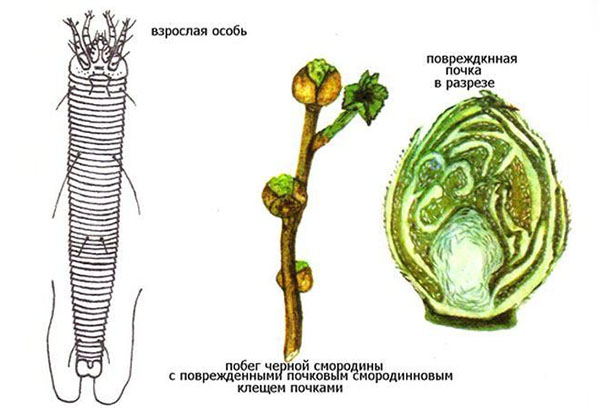
Kidney mite
It is impossible to see a currant bud mite, but traces of its activity on currant bushes are evident:
- twisted ugly shoots;
- defective ovaries, quickly crumbling;
- light underdeveloped leaves on the apical shoots.
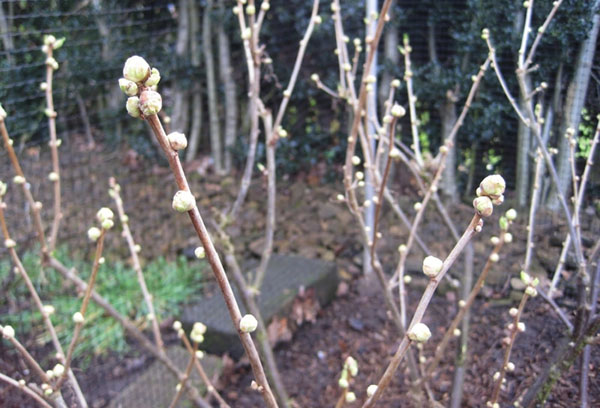
If you carefully examine the affected blackcurrant bush in early spring or autumn, then among the usual buds you can see enlarged rounded specimens. The number of infected buds depends on the size of the pest colony. In each, several fertilized tick females winters.
In spring, when the air warms up from + 5 ° C, the process of laying eggs begins. One female is capable of producing up to 8 thousand individuals after wintering and up to 40 thousand during the entire growing season of the plant. The new generation of ticks hatch around the 6-10th day and begin to intensively feed on the blossoming healthy buds.
At the time of mass flowering, pests spread throughout the site, settling not only on black, but also on other types of currants, as well as on gooseberries. It is because of the currant mite that the bushes most often become infected with the terry virus, become vulnerable to other pests and diseases.
The most effective measure of control against currant mites is the spring and autumn collection of swollen buds with their subsequent destruction.
Advice
It is better to collect buds on black currants after autumn leaf fall, since in spring there is a risk of breaking off swollen healthy specimens.
Sometimes the currant bush is almost completely affected, then it is pointless to cut off single buds. The whole bush is cut off "under the stump", the branches are burned.
In case of mass defeat of a bush by a tick, acaricidal preparations are used.Since the harvest of black currant is formed at a high rate, toxic agents are used during the budding period. Treatments are carried out in accordance with the characteristics of the life cycle of the pest.
- The first spraying is when throwing out the flower brushes (before the buds open). This is a period of mass migration of a new generation of ticks to intact buds and other bushes. Preparations: "Nissoran", "Actellic", "Vermitek", "Endidor", "Kontos".
- 8 days after the first spraying, a second one is made.
- The third treatment is carried out after harvesting the entire crop. More toxic agents are used: "Phosphamide", "Nitrafen", "Rogor-S", "BI-58", "Danitol", "Neoron", "Apollo".
Ticks do not tolerate colloidal sulfur ("Sulfaride"). But the effect of the drug occurs only in hot weather (about 27 ° C), therefore, in most regions with a cool climate, sulfur treatments will be meaningless. Moreover, both from ticks and from a fungus.
Important!
Such preparations of surface action as "Decis", "Karate", "Kinmiks" do not act on the kidney mite.
Provided it is warm and early spring, treatment of currants with bioacaricides will be effective against ticks: "Aktofit", "Akarin", "Bicol", "Boverin", "Bitoxibacillin". These drugs are based on fungi and bacteria that are hostile to arachnids. The main condition for efficiency is temperature from + 18 ° С. You can use the funds during the entire growing season.
To slow down the reproduction of mites during the flowering period of currants, you can use folk methods: infusions of onion peels, garlic, tobacco. Perennial onions and garlic planted around the bushes will have the same effect.
Blackcurrant sawfly
The sawfly makes clutches of eggs on black currants already during the period of ovary formation, and chooses the largest of them. The first sign of damage is prematurely ripe berries. The reason is seeds eaten by sawfly larvae.
The best way to keep the caterpillar from going outside and then hiding in the soil is to collect any suspicious berries and destroy them. If the lesion is large, it can be treated with Agrovertin or Fitoverm.
Goose moth
Pupae of the moth hibernate directly under the currants, moving to a bush for laying eggs in the spring. The larva gnaws one flower after another, leaving behind a cobweb. Such brushes must be collected and destroyed.
If in the previous summer a moth was seen on black currant, then the fight against it should be started the next season in early spring.
- Before the snow melts and the beginning of flowering, you need to cover the soil around the bush with a film. So the pest will not be able to come out. You can remove the shelter after the first ovaries appear.
- Before flowering, currant bushes should be treated with Karbofos.
- With the beginning of flowering, spray with "Agrovertin" or "Fitoverm".
Thus, you can get rid of the pest for the entire season.
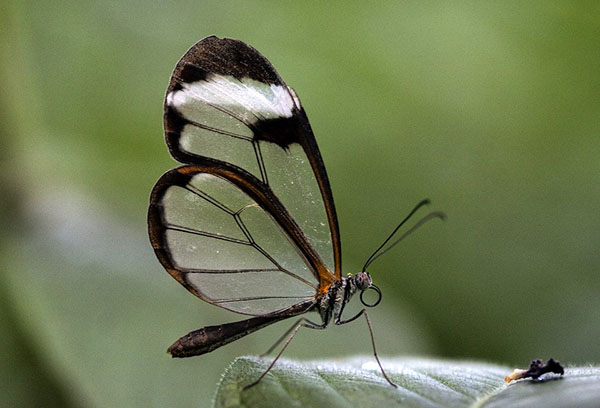
Glass-maker
Glass butterflies lay their eggs on black currant shoots from the second half of June to mid-July. The clutches are located near the kidneys, next to the potholes in the bark. Caterpillars emerging from the eggs penetrate into the shoot and gradually eat away at its core, replacing the tissues with their excrement. As a result, next year, during the flowering period of currants, one can notice wilting, and then the death of individual branches.
In spring, all affected shoots should be cut to healthy wood and then burned. After flowering, the bushes must be sprayed with "Fitoverm" or "Aktara" (1%).
Advice
Coriander sown around the bushes will help scare off the pest from the currants.
Gallica
Gall midge is a small fly-like insect. These black currant pests are divided into three types.
- Shoot gall midge, whose larvae destroy new shoots. Exit during mass flowering.
- A flower gall midge laying eggs in buds. Exit during the ejection period of the brushes.
- Leafy gall midge affecting young leaves.Exit at the beginning of the disclosure of flowers.
Spraying will help to get rid of this pest: before flowering - "Fufanon", during the entire growing season - "Fitoverm". You can get rid of the second generation by treatment with "Karbofos" 2 weeks after all the berries are harvested.
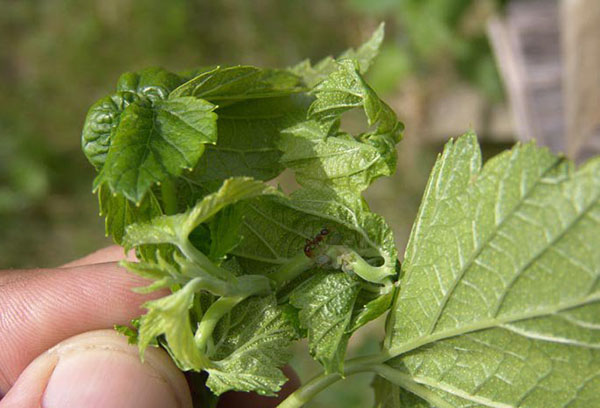
Sprout aphid
This small pest with a delicate body is clearly visible to the naked eye. Young shoots of currants stop growing, leaves curl, not having time to straighten out. Aphids plant densely on the tips of branches and on the back of young leaves. The reason for its appearance is not only flying females, but also garden ants, so you should fight them too.
Chemicals in the fight against aphids do not need to be used. Treatment with "Fitoverm", "Iskra-bio" is quite effective. Many gardeners gently wash the tips of currant branches in a solution of household or special "Green" soap. One female lays about a hundred eggs at a time, so fight aphids will have to constantly. Fitoverm is able to protect the currant bush for up to 3 weeks.
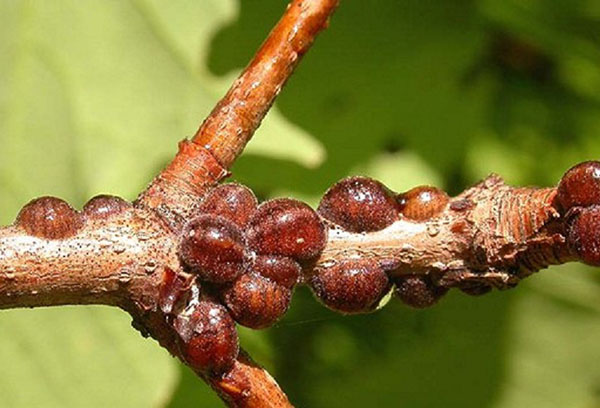
False shield
When damaged by a false shield, currant shoots are covered with small brown oval outgrowths. With a small amount, they can be scraped off with a knife, after having laid a film under the bush. Spraying with "Fitoverm" is effective, which penetrates even through the strong chitinous cover of the pest. In late autumn, the berry should be treated with a urea solution: 400 g per 10 liters of water.
Diseases
In addition to pests, black currants are often attacked by diseases: fungi and viruses. Fungal infections can be dealt with by treatments and agrotechnical methods, but these methods are powerless against viruses. These include terry (reversion). If you find shaggy open flowers with purple petals on a black currant, the bush should be dug up and destroyed. It is a terry virus that renders the plant sterile. Instead of flower brushes, green panicles appear. The disease cannot be cured, but it is actively transferred by sucking pests.
Fungal diseases also often affect currants.
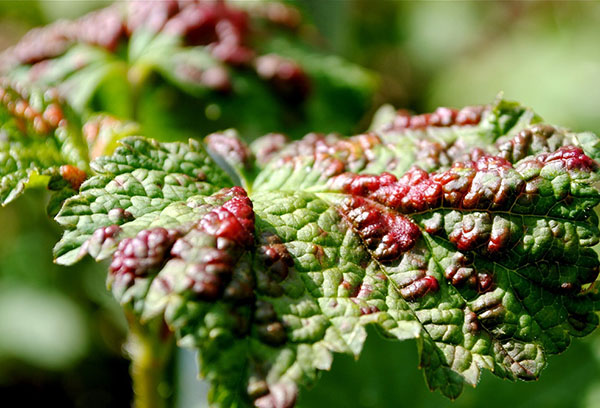
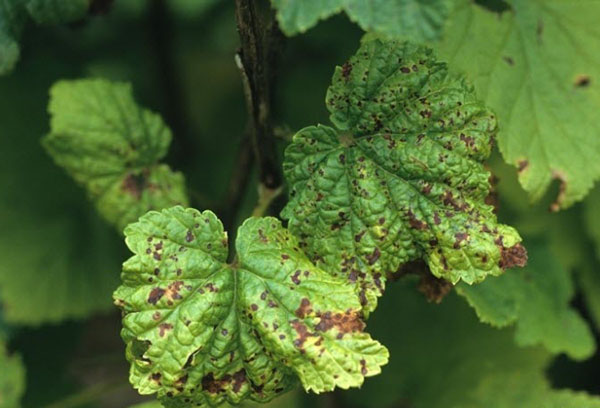
- Anthracnose. The first sign of damage to currants is the appearance of small brown spots on the leaf plate. Gradually, they merge, as a result, the sheet dries and curls. Outwardly, such a bush looks like a burnt one. By August, the currants can completely lose their leaves, which leads to the weakening of the plant.
- Columnar rust. It attacks currants from about mid-summer. The presence of pine or cedar on the site increases the risk of disease. The disease manifests itself as yellow spots on the outside of the leaf and loose orange bumps on the back.
- Goblet rust. The disease can be recognized by the appearance of a yellow-orange crumbly coating on the leaves of the currant. Gradually it becomes denser, the leaf dries up and dies off.
- Septoria. Currant leaves are covered with small rounded spots with a white center and brown edges. Gradually they merge, forming extensive brown smudges.
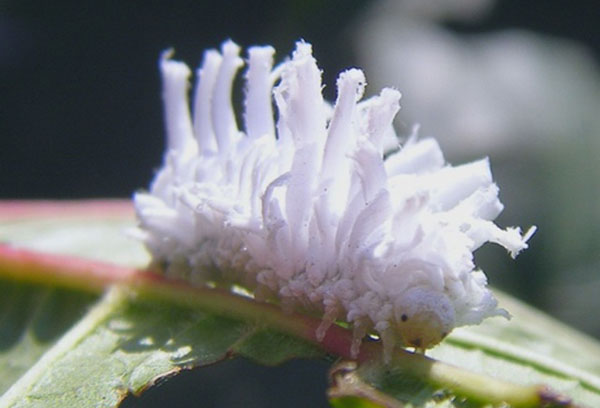
- Powdery mildew. The disease manifests itself as a white soft bloom on the leaf plate. As the mycelium darkens, the leaf dries up.
The frequency of outbreaks of fungal infections largely depends on the weather and climate in general. General methods are applicable to combat them. The disease is far from always possible to defeat during the growing season, often the bush remains bare in August. An important contribution to the victory over the fungus next season is a thorough harvesting of plant residues in the fall. To do this, collect and destroy all the leaves, weed the trunk circle, treat the bush and soil with antifungal agents. The following drugs are suitable:
- Bordeaux liquid (3%);
- copper oxychloride;
- iron vitriol (3% solution);
- copper sulfate (50 g per 10 l of water);
- "Zircon";
- urea solution (300 g per 10 l of water);
- Fundazol;
- "Nitrafen";
- "Topaz".
Autumn treatment against fungus ends with mulching of the trunk circle.
In the spring, before bud break, currants are sprayed with Bordeaux liquid (1%), iron vitriol. After flowering, if there are signs of the disease, the bush can be treated with colloidal sulfur (1% solution), Bordeaux liquid, pink manganese solution.
Important!
Iron sulfate is just as active against fungus as copper sulfate, but less toxic.
For prophylaxis during the entire growing season, currants and the ground under it can be sprayed with "Fitosporin-M" (once every 2 weeks).
To protect against fungal infections, such biological products are effective:
- "Riverm";
- Trichodermin;
- "Fitodoctor";
- Mikosan.
To minimize the risk of yield loss, the least susceptible varieties should be planted.
Currant, relatively resistant to diseases and pests:
- Binar;
- Kipiana;
- Katyusha;
- Memory of Vavilov;
- Titania;
- Ceres.
The choice of a means for processing black currants is largely determined by the prevalence of a pest colony or disease. If you can get by with manual collection of larvae or processing with biological products, then it is better to refuse the use of toxic agents during the growing season. In advanced cases, pest control will require punctuality and patience to complete the whole range of work.
















and will be published shortly.