Beet planting technique in open field and aftercare
Beetroot (beetroot) is one of the most popular root crops grown in personal plots. There are two ways to plant beets: seeds and seedlings. There is no fundamental difference between them. The yield mainly depends on the structure and fertility of the soil, and many varieties of beets are quite loyal to weather conditions. If you correctly make a ridge, then you can get high-quality fruits in a drought and in a rainy summer.
Soil and bed preparation
When choosing a place for beets, you should pay attention to what crops occupied the planned area last season. Planting this root vegetable is categorically not recommended after cabbage, but after potatoes, cucumbers, zucchini, pumpkin and greens, the beet will grow well. Carrots, peas and onions are neutral precursors. When growing beets on an industrial scale, they are planted after winter wheat and rye.
The beets are planted in a well-lit place for a long time. There should be no dense bushes, spreading trees, fence, walls nearby. It is advisable to choose a high part of the site that is not flooded by torrential rains.
It is worth considering the basic requirements for the soil for beets.
- Acidity in the range of 6.2-7.5. If there is a lot of colza, wild sorrel and horsetail on the site, then the soil is acidic. Root vegetables will be small, ugly in shape. Lime or dolomite flour must be added. When preparing a ridge for beets, moderate liming is possible in the year of planting.
- The optimal soil is loose, rich in organic matter (loamy, sandy loam, black soil). Growing beets in too clayey soil without special preparation and application of sand is a waste of time and effort. The fruit will be fibrous, tough, and bitter.
- The depth of the arable soil layer is from 25 to 30 cm.
Under favorable conditions, root crops develop quickly, and an accelerated accumulation of sugar occurs.
Advice
Excessive lime content in the soil leads to a decrease in the ability of beets to absorb micro and macro elements. It is important to respect the dosage.
Fertilization
Beets are demanding on the content of micro- and macroelements in the soil. For reference: 1 ton of root crops extracts from the ground up to 7 kg of nitrogen, about 3 kg of phosphorus and up to 9 kg of potassium. While the root system is still weak, the plant especially needs phosphorus, then intensive absorption of other nutrients begins.
It is optimal to prepare a ridge for beets in the fall, adding rotted manure, compost (about 15-20 kg per 1m2) and phosphorus-potassium fertilizers. Mineral dressings can be embedded in the soil before planting. Of the complex additives, NPK 13-12-19 or CAS.
For winter sowing of beets, the following complex of fertilizers is introduced into the soil (per 1 m2):
- half a bucket of manure, humus or compost;
- 30 g of potassium chloride (chlorine ions prevent the accumulation of nitrates);
- 30 g superphosphate.
Advice
Beets are very fond of organic matter, but the introduction of fresh or semi-rotted manure before planting will lead to a deterioration in the taste and presentation of the fruit.
In preparation for planting, the soil is carefully dug to a depth of about 30 cm, all clods are broken, the surface is leveled and slightly compacted. Many gardeners plant beets along the ridges - long, high ridges like potato ones. Thus, the root crop is better ventilated, receives more sun, and is protected from rot and souring. This is especially true for heavy soil. If the soil is fertile and loose, then carpet can be planted.
Landing dates
Beet seeds can also germinate at temperatures of 3-4 ° C, but the process will take about 25 days. At 6-7 ° C, seedlings will appear already on the 10-15th day, and when the temperature stabilizes to 11-18 ° C, the period will be only a week. There is no point in sowing beets until the soil at a depth of 6 cm warms up at least to 7-8 ° C, since there is a high probability of death of seedlings from frost (the sprouts will not tolerate -1 ° C).
Planting beets in spring in different regions is carried out at their own time:
- North Caucasus - 1 decade of April;
- Central Black Earth Region - 3rd decade of April;
- north of the Central Black Earth Region, Non-Black Earth Region, Volga Region, Bashkortostan and Altai - 1 decade of May.
Long-term storage late beets are sown in the second decade of May; they can be planted until June 10. Such varieties will have enough time before frost to fully mature, and they are stored much better than early and mid-season ones.
The terms are given roughly, for each year they may vary depending on weather conditions.
You can sow beets in a greenhouse or in boxes about a month and a half before planting in open ground. The scheme of embedding into the substrate: 4 x 4 cm. This method is suitable for regions with unstable weather. The ripening period of root crops with the seedling method of growing will accelerate by 2-3 weeks.
You can plant beets with seeds in the fall. There are special varieties for this, since ordinary species will begin to shoot and will not yield a harvest. Sowing beets in autumn is beneficial for regions with cool, short summers. The sowing date comes when stable frosts begin, the soil is covered with a crust. In the Urals or Siberia, the right time is November. There are no general recommendations from what date to sow beets in the winter. It is important not to miss the last period before the earth "grabs" (3-4 ° C below zero). According to popular observations, the optimal time is the moment when the leaves are completely shed by the cherries.
It should be noted that autumn planting beets are not suitable for long-term storage.
Seed preparation
Beet seeds are fruit lumps, in which several seeds are collected (from 2 to 6 pieces). For this reason, many novice gardeners are surprised when, with a neat schematic sowing of seed-capsules, heap shoots suddenly appear from the garden bed.
Beet seeds planted in spring will hatch faster when prepared. The easiest way is to soak for a day in a solution of one of the following products (for 1 liter of warm water):
- a quarter teaspoon of boric acid and half a teaspoon of nitrophoska or nitroammophoska;
- 1 teaspoon superphosphate;
- a teaspoon of baking soda;
- a tablespoon of wood ash.
A day later, the seeds are washed, wrapped in a damp cloth and kept at room temperature for 3-4 days, not allowing the bundle to dry out.
For autumn planting, you do not need to soak the seeds.
Sowing technique
Immediately before the spring planting of the beets, the ridge is loosened about 5 cm deep and leveled. Sowing or planting seedlings is necessary either in cloudy weather or in the evening, so that the soil does not wind up and the seedlings do not die from the hot sun.
Planting beets in open ground with seeds is carried out according to the following rules:
- rows are made at a distance of at least 30 cm;
- on loam, beet seedlings are embedded in grooves 2-3 cm deep;
- on sandy and sandy loam soils - 3-4 cm.
In dry weather, the ridge is poured with water in advance (for an hour or two), in rainy weather it is enough to moisten the grooves. After 3-4 days, it is recommended to loosen the soil with a spring or wire rake. After this procedure, the beets grow more friendly.
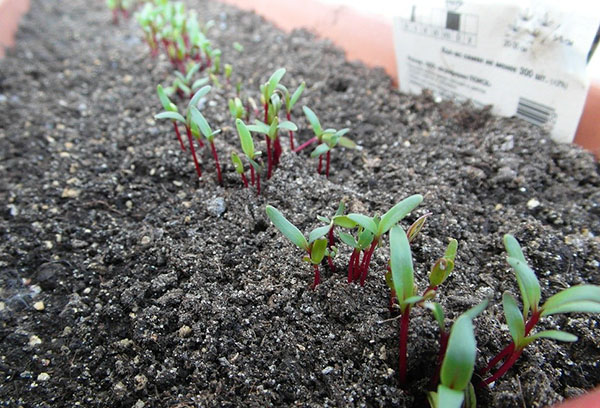
When shoots appear, they must be carefully thinned out. This procedure is carried out twice: in the phase of two true leaves, leaving a distance between the seedlings of 3-4 cm, then in the phase of 3-4 leaves. The average gap between beet sprouts should eventually be 10-20 cm.How much to leave depends on the variety, usually the step is indicated on the seed package.
Advice
If you leave too large gaps between the plants, then the roots will grow large, difficult to heat treatment.
Excess beet sprouts should not be thrown away. If you spill the soil well before the procedure, and pry the seedlings with a special spatula (you can use a spoon handle), then the roots will not be damaged. The seedlings will quickly take root in another place, and the shape of the fruit will not suffer in the future, as is the case with carrots.
Podwinter sowing of beets is carried out in dry soil. The seeds are placed in grooves 4 cm deep and covered with a loose substrate (you can mix the earth with sand). Then the soil is slightly compacted, the bed is mulched and covered with dry leaves or spruce branches. In the spring, the shelters are removed, the soil is spilled with nitrogen fertilizer, and a film is laid on top until the first shoots appear.
Care
The main care for young beet sprouts is to moisturize and loosen. A crust must not be allowed to form on the soil. Loosening is done carefully, while the plants are small, you can do this with an ordinary old fork. Beets are responsive to this procedure, therefore it is recommended to carry it out until the foliage closes.
Top dressing
The first feeding of beets with mineral fertilizers (nitrogen) is carried out after thinning, the second (complex) - after closing the tops.
Nitrogen, potassium and phosphorus are the main elements needed by beets. If there is no complex mineral fertilizers at hand, then ash, previously mixed with compost, can be added to the soil. Consumption: 3 glasses of pure ash per 1m2.
Advice
Nitrogen fertilizers for beets it is better to add in several portions and not overuse, since their excess contributes to the accumulation of nitrates in root crops. Fractional application reduces the negative effect by 2 times. The best form is urea (10 g per 1 m2).
The second feeding beets (when the fruit is about the size of a walnut) consists of potash-phosphorus fertilizers. Consumption: 8 g of superphosphate, 10 g of potassium chloride per 1 m32... Nitrogen is no longer used.
If there is not enough boron in the soil, then the beets react by rotting the core. The deficiency of copper and molybdenum is also negatively affected, which can be replenished with foliar feeding (in the 10-leaf phase). For this, liquid micronutrient fertilizers are used, which contain boron in organomineral form and manganese in chelated form.
If the beets develop slowly, rounded yellow spots appear on the tops, then there are signs of a lack of potassium and too acidic soil. In this case, watering with milk of lime will help. Recipe: 200 g of fluffy lime, 80 g of potassium chloride, diluted in 10 liters of water. The solution should be enough for 10 running meters of planting (along the line).
In case of reddening of the beet tops (sodium deficiency), it is necessary to sprinkle the ridge with ash and sprinkle with salt water (1 glass of salt per 10 liters). This procedure will also increase the sugar content of the roots.
Watering
Watering modebeets depends on the weather. In the first month and a half of plant development, the soil should not be allowed to dry out. Young beets are very fond of evening sprinkling. After this procedure, the tops freshen up and acquire a high turgor.
If the summer is not too hot, then growing beets outdoors will not be a hassle. After the tops are closed in the aisles, the moisture will erode more slowly, and the root crop is already able to get food from the deeper layers of the soil.
Watering the beets stops about a month before harvesting.
Diseases
Competent agricultural technology minimizes the likelihood of beet diseases caused by soil quality. Increased acidity is the cause of root defects, such as:
- scab in the form of cracks and growths on fruits;
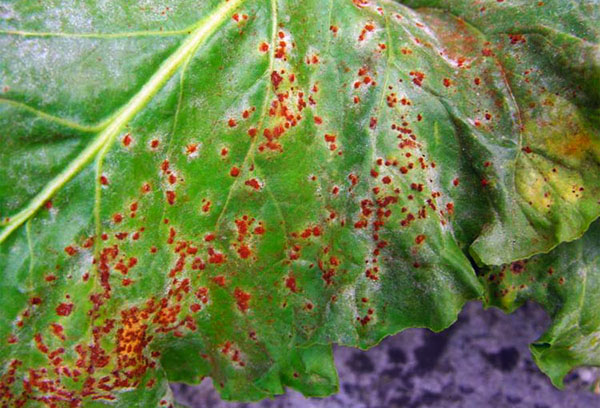
- phomosis (zonal spot on the leaves) - the disease can also be the result of a lack of boron;
- blackening of the pulp;
- root-eater, “black leg” (at the seedling stage);
- voids in the root crop.
However, all of the above can also occur due to an excess of nitrogen or with unbalanced feeding, therefore, fertilizer must be applied correctly.
Fungal diseases can develop: peronosporosis, cercosporosis, manifested by drying of the tops. Only treatment with fungicides (HOM, Fundazol, Carbendazim, copper oxychloride) can help.
Pests
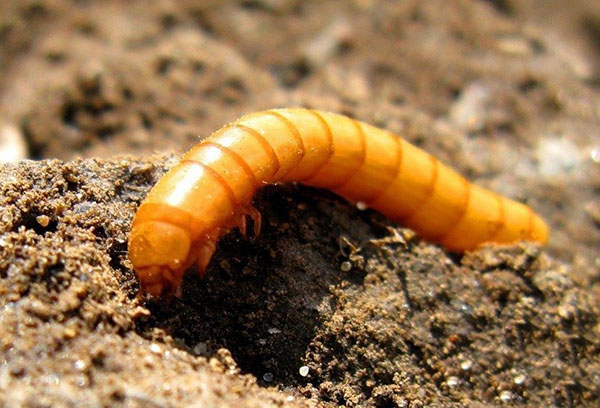
Growing beets in the country can be unsuccessful for years if wheatgrass grows around the garden and the soil is acidic. This is the most comfortable habitat for the larvae of the click beetle - wireworms... It is they who are able to turn any root vegetable literally into a sieve.
It is possible to reduce the number of these pests of beets only by regularly used control methods:
- select yellow worms manually when digging:
- bury potato tuber traps;
- exterminate wheatgrass, calcify the soil;
- periodically use special equipment (for example, "Provotox" granules).
Leaf and root beet aphids can also cause damage. Regular spraying with Green Soap solution, Pyrethrum will help to destroy the pest.
Beet fleas eat away the leafy pulp. In the fight against them, ash, tobacco dust, pollination with Hexachloran is effective.
If white winding passages appear on the beet leaves, then the larva of the miner moth lives in them. With a small scale of damage, the leaves break off and are destroyed. In case of mass infection, treatment with the drugs "Fufanon", "Bi-58 New" is used.
In most cases, growing beets in private plots is not a big deal. If there are few weeds, and soil cultivation in spring and autumn is done correctly, then the risk of attack by pests is minimal. Crop rotation is also an effective protection measure.
Many gardeners plant both late and early beets in the plots, providing themselves with a fresh harvest and a supply of root crops for the winter. This is an unpretentious plant, the seeds of which sprout quickly enough, the seedlings are patient to adverse weather conditions, and to get a good harvest, it is enough to competently prepare the garden bed.














and will be published shortly.