How to plant boxwood (buxus) and what care does it need?
With properly organized boxwood planting and caring for this plant, you can get a wonderful evergreen garden decoration. The unpretentious handsome man will perfectly complement the most exquisite design solutions of the infield.
Description of the plant
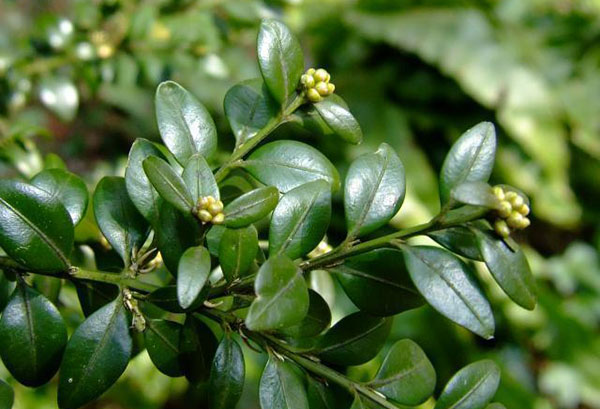
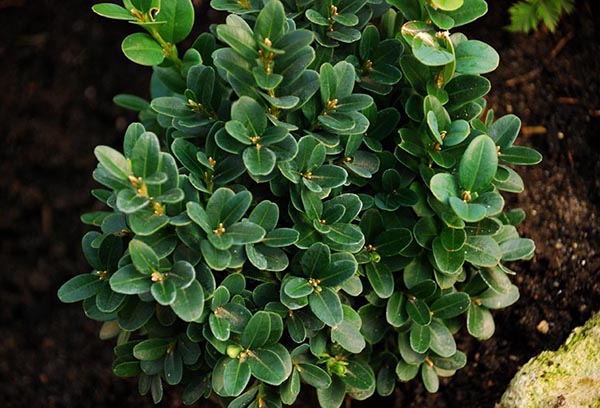
Boxwood evergreen (buxus sempervirens) is a genus of evergreen shrubs and small trees from the Boxwood family. Under favorable conditions, the plant can live up to 600 years. Buxus grows slowly.
Small, succulent leaves are elliptical and have a characteristic odor. Most species have green foliage, but variegated varieties are also available. Spikelets of greenish-yellow flowers appear in the leaf axils in March or April. They are inconspicuous and fragrant. In place of flowers, boxes with black seeds are formed. Over time, these fruits crack, and their contents scatter around.
Variety of varieties
Boxwood is used for outdoor cultivation and indoor floriculture. About 30 species of this plant grow in various regions. Numerous varieties differ in growth intensity and appearance.
- Slow-growing varieties are suitable for the formation of small sheared figures and balls Suffruticosa and Blauer heinz... The second option has another important advantage - high frost resistance.
- Buxus sempervirens - a wild type of evergreen boxwood for tall hedges.
- Strong growing varieties are also suitable for large plantings. Rotundifolia and Handsworthiensis.
- Elegantissima - a beautiful variegated variety, sensitive to low temperatures. It is better to plant this variety in an area protected from the wind and carefully cover it for the winter.
- Some slow-growing varieties of boxwood make wonderful bonsais - indoor "potted trees". For these purposes, use, for example, Buxus harlandii Hance.
Reproduction of buxus
There are three ways to get new specimens of an evergreen.
- Cuttings.
The easiest and most affordable breeding option. The best time for such an operation is July or August. Young bushes planted during this period will have time to take root well and get stronger before frost. This will help them get through the winter easily. You can carry out cuttings in September, but then the survival rate of the buxus decreases.
The beds for young plants are pre-dug, weeds are removed and the soil is watered abundantly. The site should be in shade or partial shade. The soil is needed clay and loose, with a high humus content.
Choose branches with a length of at least 20-30 cm. Cuttings are harvested by cutting off one- or two-year-old shoots at an angle with pruners or sharp scissors on a box tree just before rooting. The workpieces must not be placed in water or dried in the sun. The shoots are shortened by removing a third of the cuttings. Leaves are left. Then they are planted in a place protected from the wind in partial shade. The spacing between plants is about 8 cm, the row spacing is about 15-20 cm. Young plantings do not need to be covered with film, the ground around them is slightly compacted.
In autumn, the bushes will reach a height of about 15 cm. They need to be covered with leaves for the winter, and in the spring they should be placed in a permanent growing place.
When carrying out cuttings in the fall, the rooted bushes can be transplanted into a container of a suitable size and transferred to a cool place for the winter until spring.
- Reproduction by seeds.
The seed is pre-soaked in water for a day, it is desirable to add a growth stimulator to the liquid. The seeds are then placed on a damp cloth and kept in a warm place. Do not allow the material to dry out. After about a month, the first shoots hatch. They are sown into the ground from equal parts of peat and sand. The seeds are placed in the ground, directing the sprouts down. Cover with glass or plastic wrap and put away in a warm place without access to the bright sun. Seedlings appear in about 15-20 days. After that, the glass or film is removed and regular maintenance is provided: timely watering, loosening and feeding with a very weak solution of fertilizers. They are transplanted into open ground when there is no threat of return frosts.
- Layers.
In the spring, branches located near the surface of the soil are pressed to the ground. They need to be fixed and sprinkled with soil a little. Layers are watered all summer. It can be planted when the root system is formed and the "baby" begins to grow.
How to plant boxwood correctly?
It is believed that the best time to plant boxwood in open ground is from mid-September to early October. In this case, before the onset of frost, the plant has time to root well. However, some gardeners plant the buxus in both spring and summer. Pre-prepare the site: carefully dig up and level the soil, remove weeds and, if necessary, add compost.
Small copies of the buxus are sold in containers with soil or with an open root system. The seedlings are pre-placed in a bucket of water for a day. Planted after sunset or on a cloudy day. Large pits are prepared in which the roots will easily spread. Sand, leaf humus and sod land are placed at the bottom in a ratio of 1: 4: 2.
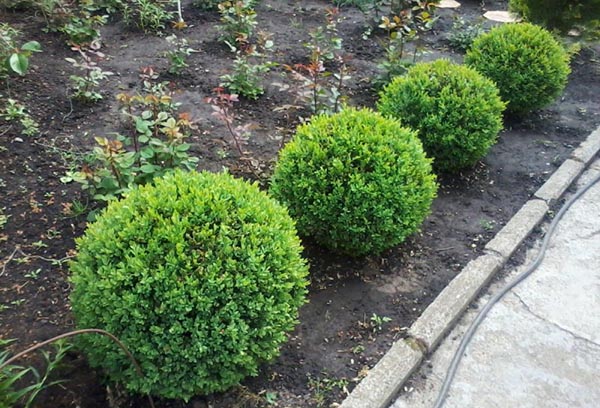
The spacing between plants when planting will depend on the type of boxwood and how the bush is used. To form a border per square meter, about 10 young plants about 13 cm high are planted. The bushes are watered and shortened by a third.
Bushes need about a month to root. During this time, they should be watered weekly, the ground should be constantly moist. Gradually, the number of irrigations is reduced, and at the beginning of summer, for the first time, they are fed with complex fertilizer.
Gentle young tugs are recommended to be planted in open ground in autumn. Seedlings older than three years are less whimsical, they can be placed in the ground at any time of the year, except for winter.
Cultivation secrets
Buxus is an unpretentious plant. In leaving, you should follow simple rules.
- It is better to underfill than overflow - it is a drought-resistant shrub. However, if boxwood grows outdoors in a pot, then in dry hot weather it will have to be watered almost daily. The plant is sprayed from time to time.
- Buxus is resistant to cold, but shelter will be required if the temperature drops below -20 degrees in winter.
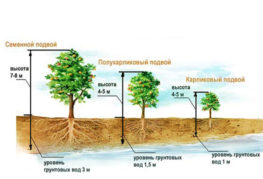
- You need loose soil with good drainage and neutral acidity. Loamy soil containing lime is best suited. Mature compost is additionally introduced into the depleted sandy soil. Soil with a high groundwater level and areas where water stagnates for a long time after rains will not work. Excess moisture can lead to root rot.
- The plant does not like direct sunlight and hot southern parts of the garden. In such a place, the leaves are quickly damaged, the buxus may even die. It is better to plant an evergreen handsome man in partial shade.
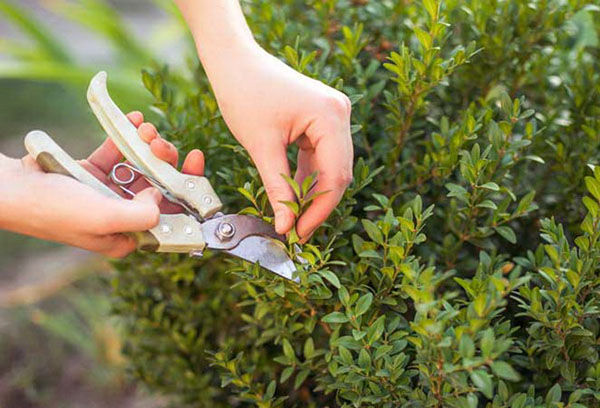
- Pruning is an important part of boxwood care. It is carried out with sharp garden shears about once a month from April to September. The more often you trim an evergreen handsome man, the thicker and more magnificent its crown will be. As a result of shortening, the plant loses some of the nutrients that were located in the cut branches. The more often a plant is reduced in size, the more moisture and nutrients it needs.Such specimens are watered and fertilized more than others.
- In November, water-charging irrigation of the bucket is carried out. Before the onset of frost, the bushes are saturated with moisture before the long winter period.
- In the spring, it is useful to add nitrogen-based top dressing under the boxwood, in the late spring - organic fertilizers. To increase winter hardiness, potassium is fertilized in September - it accelerates the lignification of shoots, helping the plant to better survive the winter cold.
When choosing a pinnate boxwood, you need to know that such varieties are more demanding on the conditions of detention. They are less resistant to low temperatures and other adverse factors.
Diseases and pests
Despite the fact that boxwood is a poisonous plant, some parasites can occupy it.
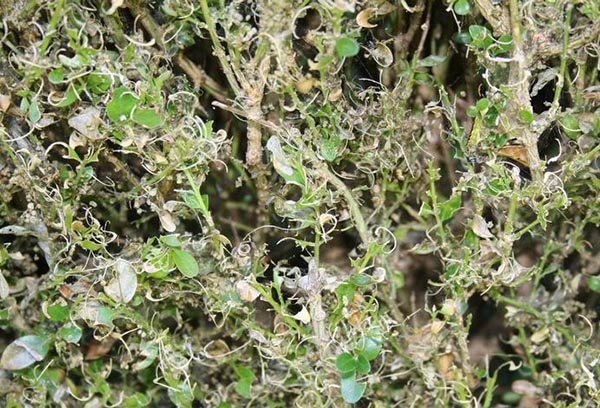
- When boxwood gall midge attacks, swellings with convex yellowish spots appear on the lower part of the leaves. The plant quickly loses its former beauty and may die if not treated.
- From a boxwood flea, the leaves become whitish and sticky.
- Buxus can also damage felt and spider mites.
- The boxwood moth loves to feast on boxwood leaves. One caterpillar completely eats a medium-sized leaf in four hours.
Several types of insects help boxwood to fight pests. Lacewing, ladybugs, predatory mites and hoverflies are the sworn enemies of aphids, scale insects and spider mites. They destroy all pests naturally, if there are few of them. In case of a massive attack of parasites, the planting is treated with a suitable insecticide according to the instructions. Effective drugs - Aktellik, Aktara, Confidor Maxi.
Usually, the development cycle of pests is longer than the time of action of the insecticide, therefore two, and sometimes three treatments are carried out with an interval of 2-3 weeks.
The plant is sprayed on both sides, it is also necessary to wet the soil under the plantings with pests. Work is best done in the evening after sunset: many chemicals at temperatures above +25 degrees are highly toxic to humans.
Boxwood branches are damaged by rust. Spores of this fungus can migrate to the plant from the pear, therefore, it is not recommended to grow representatives of Pink and Boxwoods nearby. The affected branches are removed. To prevent the disease, boxwood is sprayed with copper-containing agents, the diseased plant is treated with drugs that support immunity.
On the shoots of boxwood damaged by necrosis, the tops of the branches die off. This disease is fought with the help of fungicides. In case of cancer damage, areas with diseased wood are completely removed, and the wounds are treated with Fundazol.
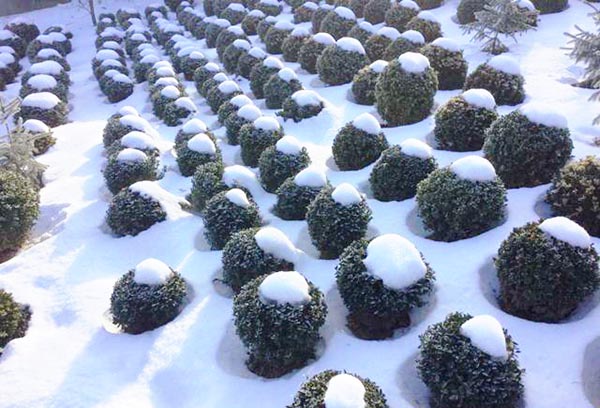
Wintering
If in winter the temperature drops below 10 degrees of frost, it is advisable to throw a cover of two layers of burlap on the curbs and hedges made of boxwood and fix it well.
Plants growing outdoors in a container should also be protected from the cold. It is convenient to use the pot-in-a-pot method. The container in which the boxwood is located is placed in a larger container. The space between the pots is filled with fine bark. The plant itself is placed on a small wooden platform.
- In the Leningrad region, the transplanting period for boxwood is shorter than in the southern regions. It is held from late April to early October. In this region, the most important time for growing a plant is winter. Care must be taken to protect the axle box from low temperatures. It is advisable to mulch the land under the plantings with needles of coniferous trees, and when the temperature drops to -10 degrees, insulate the trunk and branches. To do this, large specimens are covered with boxes of plastic or wood, and small bushes are wrapped in non-woven material and fixed.
- For many decades, varieties have been created that can be grown in Siberia, the Far East and the Urals. For example, Buxus Sempervirens can withstand temperatures as low as -40 degrees.To protect against cold winds and frost, boxwood in these regions is planted on the southern slopes. In winter, it is bent closer to the ground and covered with spruce branches. Be sure to wrap up with snow. Do this carefully so that the branches of the plant do not break.
For mulching, it is better to use coniferous needles or coniferous bark. Leaves can cause rotting.
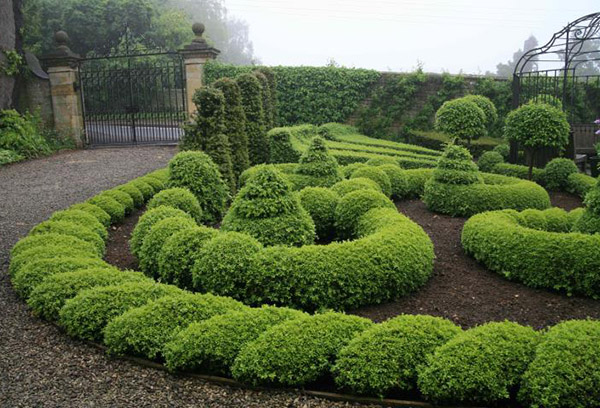
Boxwood in landscape design
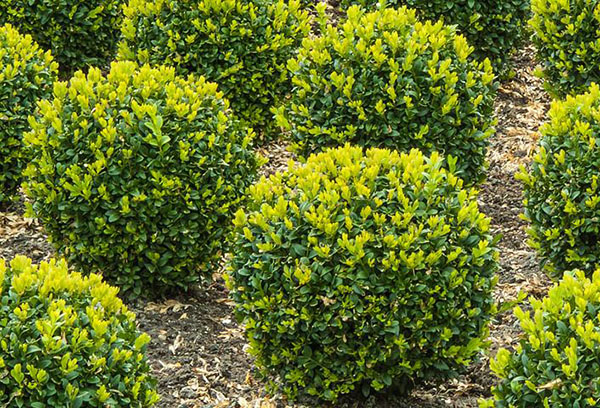
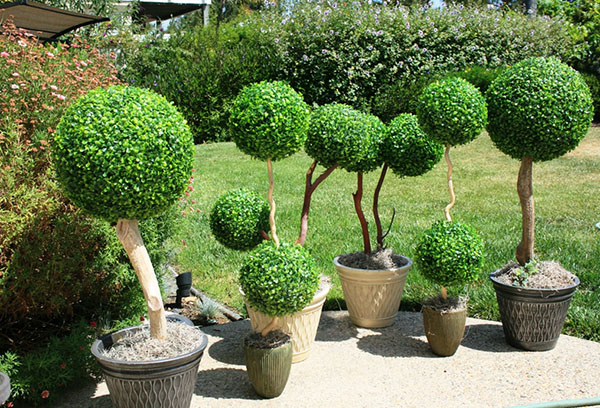
Boxwood is easily curly cut. To decorate the southern parks and gardens, artists create amazing evergreen sculptures from this plant. It is ideal for shaping curbs and hedges. A dense crown with shiny leaves is given the shape of various geometric shapes: a cube, a cone, a ball.
Boxwood can be grown as a standard tree, leaving only the central shoot of the plant.
Medicinal properties and contraindications
The chemical composition of all parts of evergreen boxwood contains many tannins, alkaloids, bioflavonoids and resins. Since ancient times, preparations from the leaves and bark of the plant have been used to treat coughs and upset stomach.
Boxwood has a diuretic, diaphoretic, hypotensive and antiseptic effect. An infusion of leaves gives an analgesic effect, with a decoction, infected wounds and abrasions can be washed. In homeopathy, buxus is used to treat infection with worms and rheumatism.
Official medicine practically does not use boxwood for the production of medicines, as it is a poisonous plant. In case of poisoning, convulsions, involuntary tremors of the limbs, cutaneous hyperemia, breathing problems, vomiting and diarrhea are observed. If the victim does not receive urgent medical attention, death from respiratory arrest is possible.
The plant is credited with mystical abilities. It is believed that a sprig of boxwood under the pillow protects from evil forces and drives away nightmares. The axle box has strong and heavy wood, which is used in joinery production.
Evergreen boxwood is the choice of those who like to enjoy greenery at any time of the year. It will become a bright spot in the garden even on the most cloudy gray days.














and will be published shortly.