Rules for planting badan and caring for it in the open field
Evergreen badan (botanical name - bergenia, folk name - star anise) from the Kamnelomkovy family serves not only as a garden decoration. It is also appreciated for its healing properties. We have collected all the nuances of planting badan in open ground and the secrets of caring for a charming perennial.
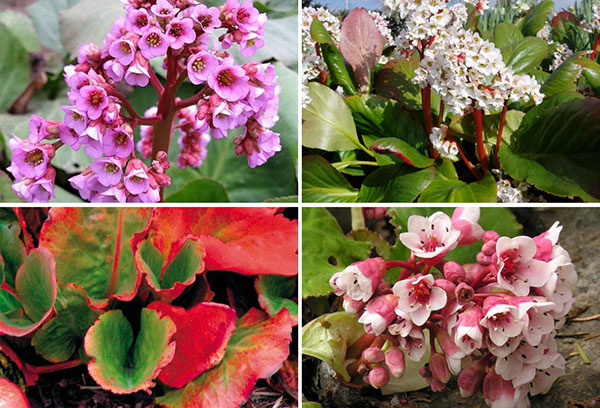
Types of badan
The natural habitat of the plant is mountainous terrain, from wooded foothills to rocky slopes over 4000 m above sea level. This is related to its drought resistance and frost resistance - adult plants tolerate frosts down to -40 ° C without loss.
The growth of badan is promoted by its creeping rhizome, from the buds of which rosette and flowering shoots are formed.
More than a dozen species have become widespread in gardening, let's get acquainted with the most popular.
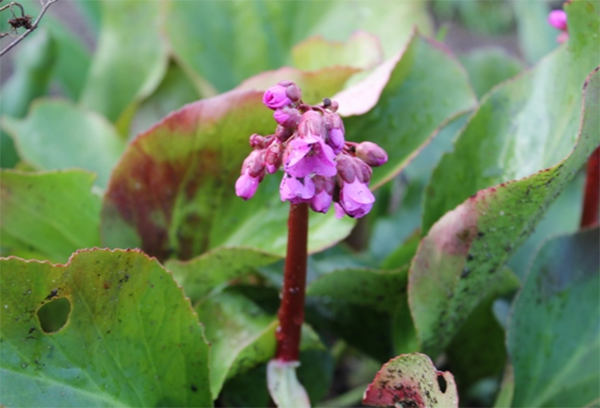
- B. thick-leaved most commonly grown. The leaves are large - about 20 cm in diameter, shiny, turn bright red in autumn. Peduncles up to 60 cm high, the size of bell-shaped flowers - up to 12 mm. The flowering period is 50 days.
For thick-leaved berry it is better to choose a place in partial shade, where it gives maximum decorative effect.
Common varieties of thick-leaved badan are Senor, Giderruspe, Purpura.
- B. pacific in its natural environment, it grows mainly in the Far East. It differs from thick-leaved in smaller size. Bright green leaves with grooved edges do not hibernate.
- B. hearty got the name from the shape of the leaves. Originally from Altai. Plant height about 40 cm, pink flowers, some varieties - white.
- B. ugamsky - endemic plant, habitat - Western Tien Shan. The species is small in number, since the optimal conditions for its growth are an altitude of more than 2.5 thousand m above sea level. Leaves are oval with jagged edges, large, up to 15 cm long. Flowers up to 2 cm in size are painted with a bright crimson color. Unfortunately, this beautiful variety is almost never found in home gardening.
- Also rare B. gissarsky and its subspecies B. Himalayan.
- B. Schmidt characterized by large (about 25 cm long) leaves, which in autumn acquire a dark red or purple color. The flowers are bright, pink with a scarlet tint.
- B. Strechi - miniature appearance, its glossy leaves, serrated at the edges, reaches 10 centimeters in length. In the wild, it grows in the Himalayas and the Pamirs. The flowers are pink and white. Among gardeners, the popular varieties Alba and Belvedere are 20 cm high and the 40-cm Beethoven variety, whose snow-white flowers are located in brown sepals on a pink peduncle.
- Berry ciliate - the name is associated with the abundance of setae covering large leaves and petioles up to 35 cm long. The toothed leaves turn bronze in autumn. Flowers are white, darken at the end of flowering. In severe frosts (below -18 ° C), the leaves freeze.
In addition to the thick-leaved, hybrid forms of bergenia are in demand among gardeners. They are distinguished by their high decorativeness and a variety of flower colors.
Leaders among hybrids:
- Abenglut - height 30 cm, purple flowers, double;
- Frau Hall - the flowers are snow-white, leaf petioles acquire a lilac color at low temperatures;
- Shneakenigin - large-leaved, the height of the purple peduncle reaches 50 cm, the flowers are white-pink, collected in long brushes;
- Baby Doll - height 30 cm, flowers of a delicate cream or pink shade;
- Tabby Andrews, especially interesting by the color of the leaves - on a green background, white and yellow spots and stripes. Height - 30 cm.
When choosing hybrids of European selection for planting in the garden, remember that they do not tolerate the winter of temperate latitudes well.
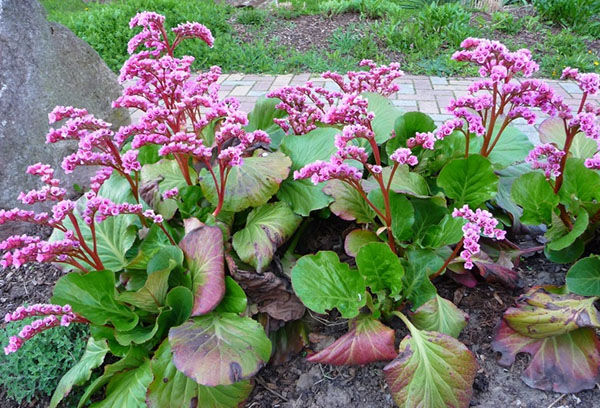
Ways of planting badan
A flower is planted in early spring - before autumn it will have time to get stronger, it will easily endure winter hardships. In the south, planting is allowed in the second half of August.
The optimal place for planting is partial shade, the sun's rays should hit the berry in the morning or evening. Full shade is a serious obstacle to flowering. Experts advise planting flowers in the southern sector of the trunk circle of adult trees: fallen leaves will serve as protection from frost, plant rhizomes will be located between the roots of the tree, absorbing excess moisture.
If the star anise grows in sunny areas, it needs more frequent watering and mandatory mulching of the soil.
Sod land is suitable for planting, where coarse sand is added. Loams are diluted with crushed stone or fine pebbles. The main thing is that the water should not stagnate in the soil, therefore, choose a place with good drainage or provide for it when preparing a site for planting.
Preparing a site for planting badan includes two mandatory stages:
- the soil is dug up to 20-30 cm;
- remove the roots of weeds and other plants.
Planting holes are dug just before planting. Their depth should not exceed 30 cm. The plant is placed in a hole, the roots are covered with earth, and abundantly watered with water heated in the sun.
Planting rhizome cuttings
The method is applicable to plants over 5 years old. It is optimal to divide in late spring.
The earth is loosened, the rhizome is carefully removed. It grows in width, so it is not difficult to separate the leaf rosettes from the mother plant. Delenki are immediately planted in prepared planting holes, covered and watered.
Saplings grow quickly, so they are planted at a distance of at least 30 cm from each other.
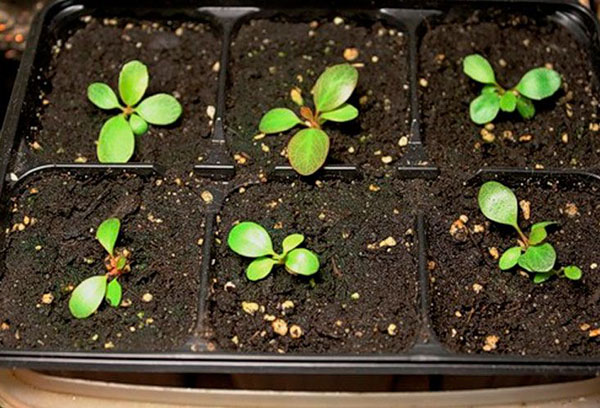
From seed
The cultivation process is long, the berry grown from seeds will begin to bloom in 3-4 years. Seeds are sown in early spring.
For germination of seeds, soil is selected that does not contain decomposing organic matter, otherwise nitrogen will be displaced from the substrate, and it will overheat, which is detrimental to seeds and young plants.
Growing Algorithm
- The seedling box is filled with a nutritious substrate and moistened.
- Make grooves under the seeds with a depth of 1 cm at a distance of 3-4 cm.
- The seeds are laid out in the furrows and covered with foil.
- For 10-12 days, the seedling box is kept in the cold (outdoors under the snow or in the refrigerator), then returned to a warm room.
- Seedlings dive when the first leaf is formed.
- The seedlings do not need feeding, but they respond with increased growth to spraying with growth stimulants.
- From mid-May, seedlings are grown in the garden, it is advisable to use the container method.
- Young plants are transplanted to a permanent place in the 2nd year in spring, in the second decade of March. Before that, they are hardened for two weeks, immediately before planting, they are watered with a solution of the mineral complex.
- Seedling holes are made up to 3 cm deep, they are staggered with an interval of 10-12 cm.
After planting, it is recommended to cover the seedlings with a film to protect them from return frosts, sun rays, and excessive precipitation.
Experienced gardeners recommend covering the soil with a layer of mulch - straw, dry compost immediately after planting the seedlings.
Young plants spend the first winter under cover - dry peat, fallen leaves are suitable.
Some gardeners practice dividing the maternal stem. The plant is dug up, the stem is cut into pieces with a sharp disinfected tool, and kept in a pale pink solution of potassium permanganate. The pieces of the stem prepared in this way are laid out in pots with nutritious soil and watered. They are planted in a flower garden when shoots appear.
Care
Badan is quite unpretentious, but so that his charm does not fade over time, you should familiarize yourself with some of the nuances of care.
- Drying out of the soil is unacceptable: the root system of the plant is weak, it is located in the near-surface layer of the soil. A layer of mulch will protect the berry from drying out.
- Water only if there is no rainfall for more than a week, but not more often than once every 7 days.
- The soil is regularly loosened, weeds are removed.
- Before wintering, the inflorescences are removed, the leaves are left - they give the roots additional protection from the cold. They are harvested in the spring.
- The bushes are regularly thinned out - this way the plant will develop better, in addition, the thickening of the plantings is fraught with the development of fungal diseases.
- Badan is fed twice a season. Fertilizer "Kemira Lux" is applied in spring. In autumn, when the color of the leaves begins to change from dark green to burgundy, - superphosphate (per square meter - 20 g / 10 l of water).
- Winter sheltered is necessary only for young plants.
- Badan is rarely transplanted; it is able to grow in one place for decades. Frequent transplants weaken the plant, reduce its decorative effect and healthiness. After transplanting, he does not form peduncles for a year or two. The optimal time to transfer a plant to a new location is from mid-summer to early autumn.
Diseases and pests
Badan is rich in tannins, which repels most insects. The exception is the slobbering penny (slobbering cicada) and nematodes.
- Folk remedies against the penny are ineffective; insecticides are used to combat it - "Inta-Vir", "Tsvetofos". Plants are treated at the end of the flowering period.
- Bi-58, Rogor, Nemathos are used against nematodes. The treatment is carried out several times with an interval of 7-10 days, since they only affect adults. An alternative to pesticides is the bio-agent "Nematofagin".
From diseases, badan is threatened by leaf spot caused by fungi. Spots appear on the surface of the leaves, white bloom on the back. The affected parts of the plant are removed, the plantings are treated with copper-containing fungicides.
Badan application
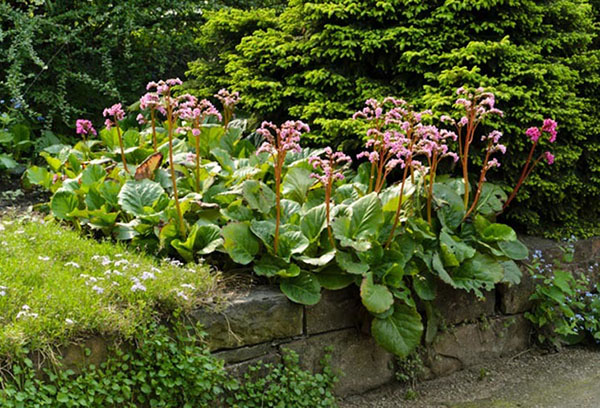
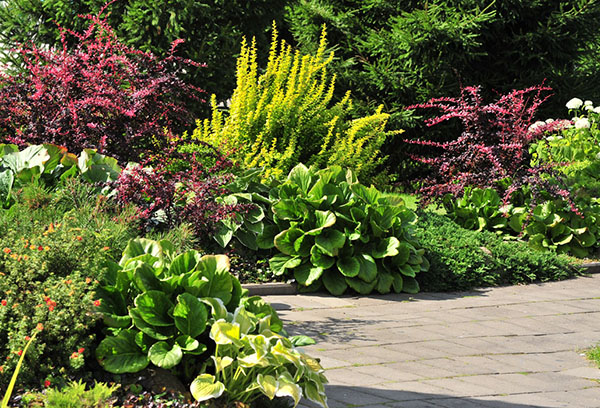
In landscape design, badan perfectly manifests itself on alpine slides, in rockeries, when decorating shady flower beds. Since his root system is superficial, they can decorate low stone walls, large boulders available on the site. By combining species and varieties, they create spectacular compositions that do not lose their decorativeness from early spring to late autumn.
The best neighbors in the flowerbed for badan:
- ferns, junipers, creating a magnificent background for delicate inflorescences;
- mahonia, evergreen shrub;
- astilba;
- helleboreblooming very early - its pale flowers look decorative against the background of the luscious greenery of badan;
- early flowering small-bulbous - crocuses, woods, snowdrops.
Plant incense next to creeping and undersized plants (lily of the valley, periwinkle), they will prevent each other from fully developing, create an indistinct flower "picture".
Badan is not only a decorative plant. Experts grow it as a medicinal raw material. On its basis, hemostatic, antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory drugs are made. Traditional medicine uses plants much more widely, including the treatment of male and female problems.
Chigir tea, popular in Altai, or Mongolian, is brewed from dry badan leaves. They are rich in vitamin C, the drink from them refreshes, tones up, lowers temperature and pressure, regulates the intestines, and normalizes metabolism.
Leaves are harvested in spring: after wintering, the amount of tannins in them is significantly reduced, they undergo natural fermentation. Tea is brewed at the rate of 2 tbsp. tablespoons of dry leaves per liter of boiling water. The brewing time is at least 15 minutes.
In cooking, dried berry rhizomes are used, which contain a large amount of starch.
Growing badan in a garden is easy, an unpretentious plant in care will decorate any corner of the garden.











and will be published shortly.